Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland becomes overactive and starts producing excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, namely T3 and T4. These hormones play an important role in controlling the rate of your body’s metabolism, and their overproduction causes many symptoms and health problems.

Hyperthyroidism is a condition that involves the thyroid gland, located at the front part of your neck, producing more thyroid hormones than your body needs. Along with this overproduction, the rate of metabolism accelerates, causing symptoms such as a racing heartbeat, weight loss, nervousness, and increased sweating.
Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, an autoimmune condition whereby the body’s immune system has decided to destroy the thyroid, thus resulting in overproduction of this hormone. Other causes include the following:
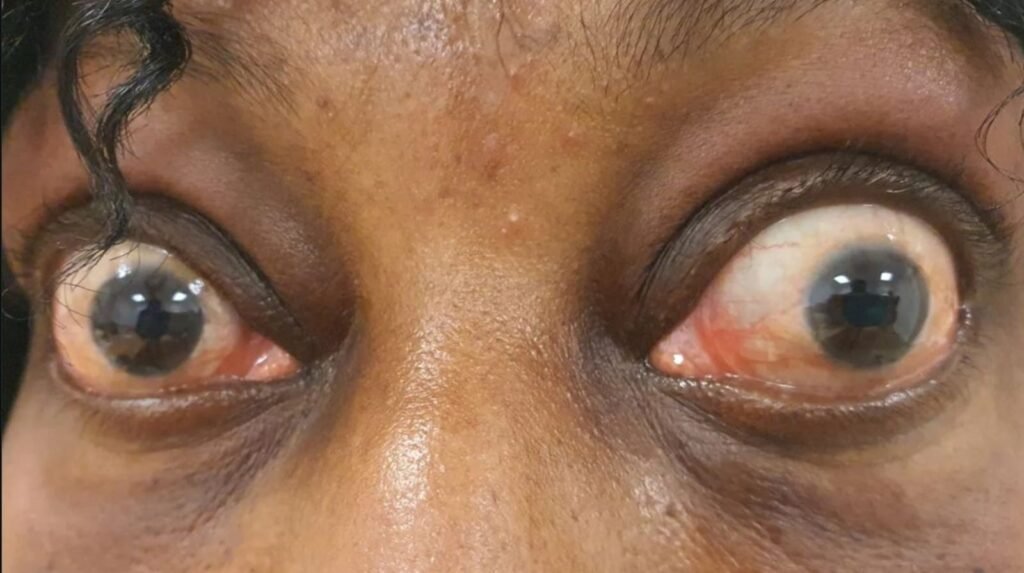
Other times, there is also an added problem with one’s eyes, such as bulging eyes, which is often related to Graves disease.
The diagnosis usually consists of a physical examination, blood tests, and imaging. Important blood tests include the measurement of the Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) level, which is normally low in hyperthyroidism, while the thyroid hormones, T3 and T4, are elevated. In some patients, a radioactive iodine uptake test or thyroid ultrasound may be helpful in establishing the cause.
The treatment depends on the cause of hyperthyroidism, severity, and general health. The options are:
1. Antithyroid Medications: Drugs containing Carbimazole and Propylthiouracil are some of the most well-known antithyroid drugs used to decrease the production of thyroid hormones.
2. Beta-blockers: These are indicated in symptomatic management-useful against rapid heartbeats and tremors-although they do not affect the total state of the disease.
3. Radioactive Iodine Therapy: The treatment is usually given orally, where radioactive iodine selectively destroys the overactive thyroid cells.
4. Surgery: If other treatments cannot be used or are not successful, surgical removal of the thyroid gland is called a thyroidectomy.
With proper treatment and management, most people with hyperthyroidism can have normal, healthy lives. It is wise to follow up regularly with your endocrinologist to monitor thyroid hormone levels and adjust the treatment if required. If you suspect that you may have hyperthyroidism or are experiencing symptoms, consult with Dr. Asif Humayun for a comprehensive evaluation and personalised treatment plan.